Your cart is currently empty.
Introduction
In recent years, pulse oximeters have gained significant attention as essential health monitoring devices. These small, clip-on devices provide instant insights into your blood oxygen levels and heart rate, making them valuable tools for managing various health conditions and monitoring overall wellness.
What Is a Pulse Oximeter?
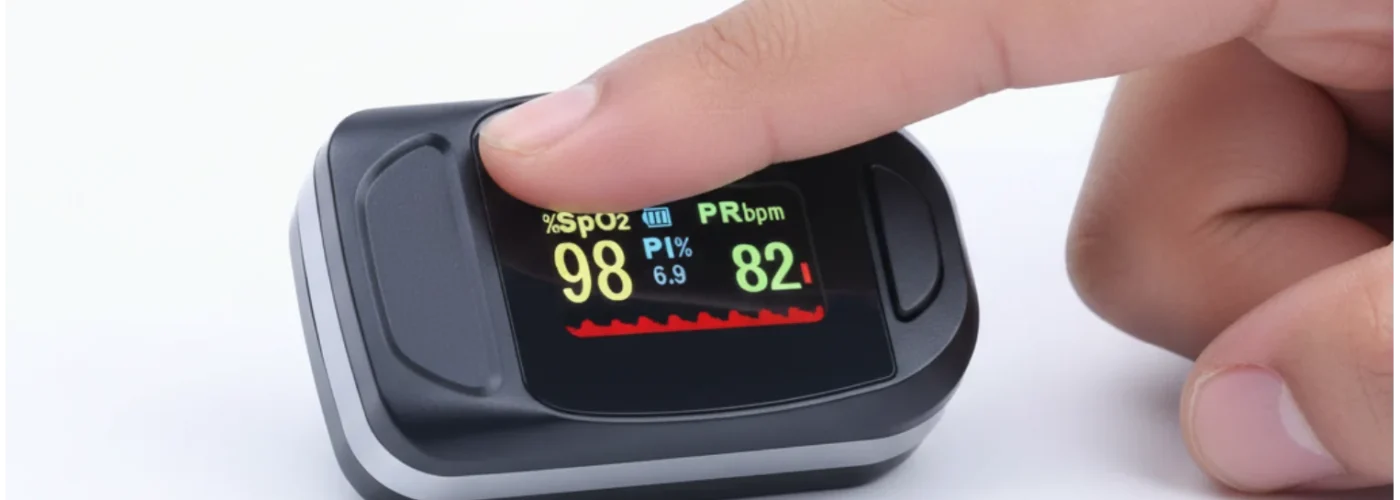
A pulse oximeter is a non-invasive medical device that measures the oxygen saturation in your blood (SpO2) and your pulse rate. The device uses light sensors to detect how much oxygen your red blood cells are carrying compared to their maximum capacity. It’s completely painless and provides results in seconds.

How Does It Work?
The technology behind pulse oximeters is fascinatingly simple yet effective:
Light Technology: The device emits two types of light (red and infrared) through your fingertip, earlobe, or toe Light Absorption: Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood absorb these lights differently Calculation: A sensor on the opposite side measures the light that passes through and calculates oxygen saturation Digital Display: Results appear on a screen showing SpO2 percentage and pulse rate
Understanding Your Readings
Oxygen Saturation (SpO2): This percentage shows how much oxygen your blood is carrying
- Normal Range: 95-100% for healthy individuals
- Concerning Levels: Below 95% may indicate potential health issues
- Critical Levels: Below 90% typically requires immediate medical attention
Pulse Rate (PR): Your heart rate measured in beats per minute
- Normal Range: 60-100 bpm for adults at rest
- Athlete Range: May be lower (40-60 bpm) due to conditioning
Who Should Use a Pulse Oximeter?
Pulse oximeters benefit various groups of people:
Chronic Condition Management:
- Asthma patients monitoring breathing effectiveness
- COPD patients tracking oxygen therapy needs
- Sleep apnea sufferers checking overnight levels
- Heart condition patients monitoring cardiovascular health
Active Lifestyle Monitoring:
- Athletes tracking recovery and performance
- High-altitude enthusiasts monitoring acclimatization
- Fitness enthusiasts optimizing workout intensity
General Health Awareness:
- Older adults monitoring respiratory health
- Parents checking children’s oxygen levels during illness
- Anyone wanting to understand their baseline health metrics
Types of Pulse Oximeters
Fingertip Oximeters: Most common type, portable and battery-operated. Perfect for home use and travel.
Handheld Oximeters: Larger devices with separate sensors. Often used by healthcare professionals and offer more detailed information.
Wrist-Worn Oximeters: Continuous monitoring devices that track oxygen levels throughout the day and night.
Pediatric Oximeters: Specially designed for children with smaller sensors and child-friendly designs.
Key Features to Consider
When selecting a pulse oximeter, look for:
Accuracy: Choose devices with proven accuracy within 2% of professional-grade equipment Display Quality: Bright, multi-directional displays that are easy to read in various lighting conditions Battery Life: Long-lasting batteries with low battery indicators Durability: Sturdy construction that can withstand regular use Ease of Use: One-button operation for quick measurements Memory Function: Storage of previous readings for trend tracking Alarms: Audio and visual alerts for readings outside normal ranges
Proper Usage Tips
For accurate readings, follow these guidelines:
Preparation:
- Ensure fingers are clean and warm
- Remove nail polish or artificial nails
- Sit still and relax during measurement
Positioning:
- Place device on fingertip (usually middle or index finger)
- Ensure proper fit without being too tight
- Keep hand at heart level when possible
Timing:
- Wait for stable reading (usually 10-30 seconds)
- Take multiple readings if results seem unusual
- Avoid taking readings immediately after physical activity
Limitations and Considerations
While pulse oximeters are valuable tools, they have limitations:
Accuracy Factors:
- Dark nail polish can interfere with readings
- Poor circulation may affect accuracy
- Excessive motion can cause errors
- Bright ambient light may influence results
Medical Considerations:
- Don’t replace professional medical evaluation
- Carbon monoxide poisoning may show false normal readings
- Certain medical conditions can affect accuracy
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact healthcare providers if you experience:
- Consistent readings below 95%
- Sudden drops in oxygen saturation
- Symptoms like shortness of breath, chest pain, or confusion
- Readings that don’t match how you feel
Conclusion
Pulse oximeters are powerful tools for monitoring your respiratory and cardiovascular health. By understanding how to use them properly and interpret results, you can take proactive steps in managing your wellness. Whether you’re managing a chronic condition, pursuing an active lifestyle, or simply staying health-conscious, a quality pulse oximeter provides valuable insights into your body’s vital functions. Remember, these devices complement professional medical care and should never replace consultation with healthcare providers for serious health concerns.