Number of items:10
Item total:₹ 16,874
Number of items:10
Item total:₹ 16,874
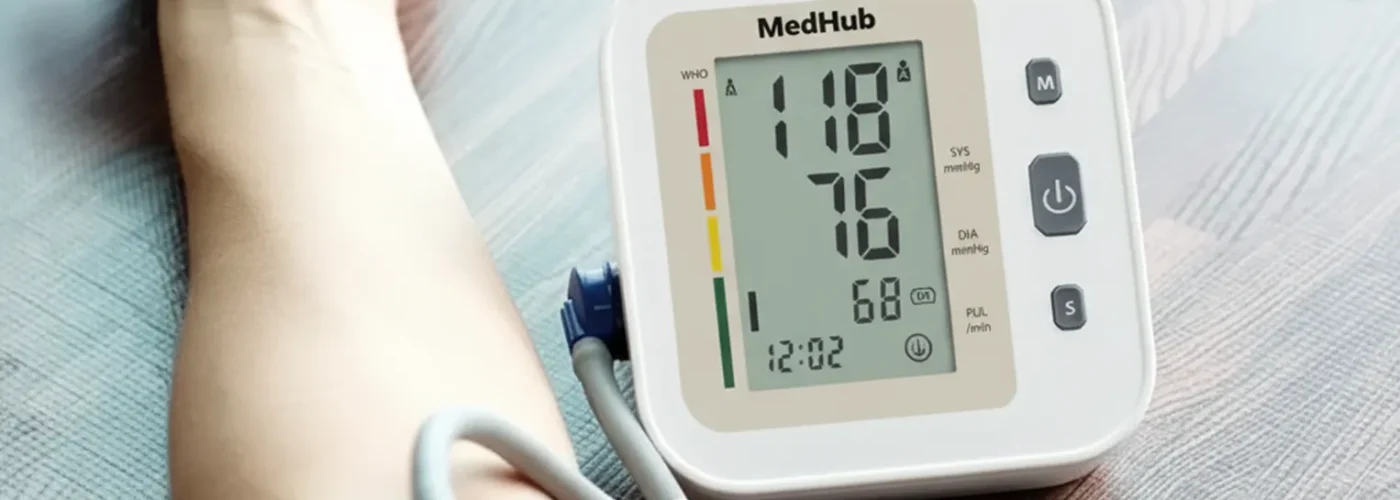
High blood pressure affects millions of people worldwide, often earning the nickname “silent killer” because it typically shows no symptoms. The good news? Monitoring your blood pressure at home has never been easier or more important. With the right blood pressure monitor, you can take control of your cardiovascular health and work closely with your healthcare provider to maintain optimal readings.
Before diving into monitors, it’s essential to understand what those numbers mean. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and recorded as two numbers:
Systolic Pressure (Top Number): The pressure when your heart beats and pumps blood Diastolic Pressure (Bottom Number): The pressure when your heart rests between beats
Normal blood pressure is generally considered to be around 120/80 mmHg. However, your doctor will provide personalized target ranges based on your individual health profile.
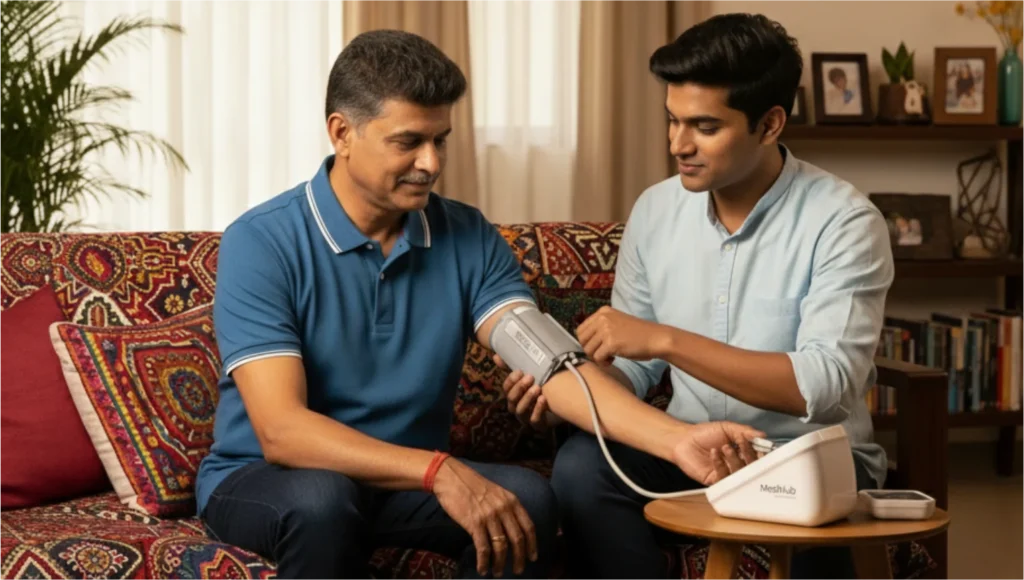

Upper Arm Monitors: These are considered the gold standard for home monitoring. They use an inflatable cuff that wraps around your upper arm, similar to what doctors use. They’re typically more accurate than other types and are recommended by most healthcare professionals.
Wrist Monitors: Compact and portable, these devices are worn on the wrist. While convenient for travel, they can be less accurate than upper arm monitors because wrist arteries are narrower and more sensitive to position changes.
Digital vs. Manual: Digital monitors automatically inflate the cuff and display readings on a screen, making them user-friendly for most people. Manual monitors require a stethoscope and are typically used by healthcare professionals.
When choosing a blood pressure monitor, consider these important features:
Cuff Size: The most critical factor for accurate readings. A cuff that’s too small or large can give false readings. Measure your upper arm circumference and choose a monitor with the appropriate cuff size.
Memory Function: Modern monitors can store multiple readings, allowing you to track trends over time. Some can store readings for multiple users, perfect for couples or families.
Averaging Feature: This calculates the average of your last few readings, providing a more comprehensive view of your blood pressure patterns.
Large Display: Easy-to-read numbers are especially important for older adults or those with vision concerns.
Irregular Heartbeat Detection: This feature alerts you to irregular heart rhythms during measurement, which could affect reading accuracy.
Proper technique is crucial for accurate readings:
Regular home monitoring offers several advantages:
Early Detection: Catch changes in blood pressure before they become serious health issues Better Medication Management: Help your doctor adjust medications more precisely Reduced White Coat Syndrome: Some people experience elevated blood pressure in medical settings Cost-Effective:Long-term savings compared to frequent doctor visits Convenience: Monitor your health on your schedule
While home monitoring is valuable, certain situations require immediate medical attention:
A quality blood pressure monitor is an investment in your long-term health. By understanding how to choose and use one properly, you’re taking an active role in managing your cardiovascular wellness. Remember, home monitoring complements, but doesn’t replace, regular medical checkups. Work with your healthcare provider to establish target ranges and create a monitoring schedule that works for your lifestyle.